¶ Strategic Manager
¶ Business model canvas (BMC)
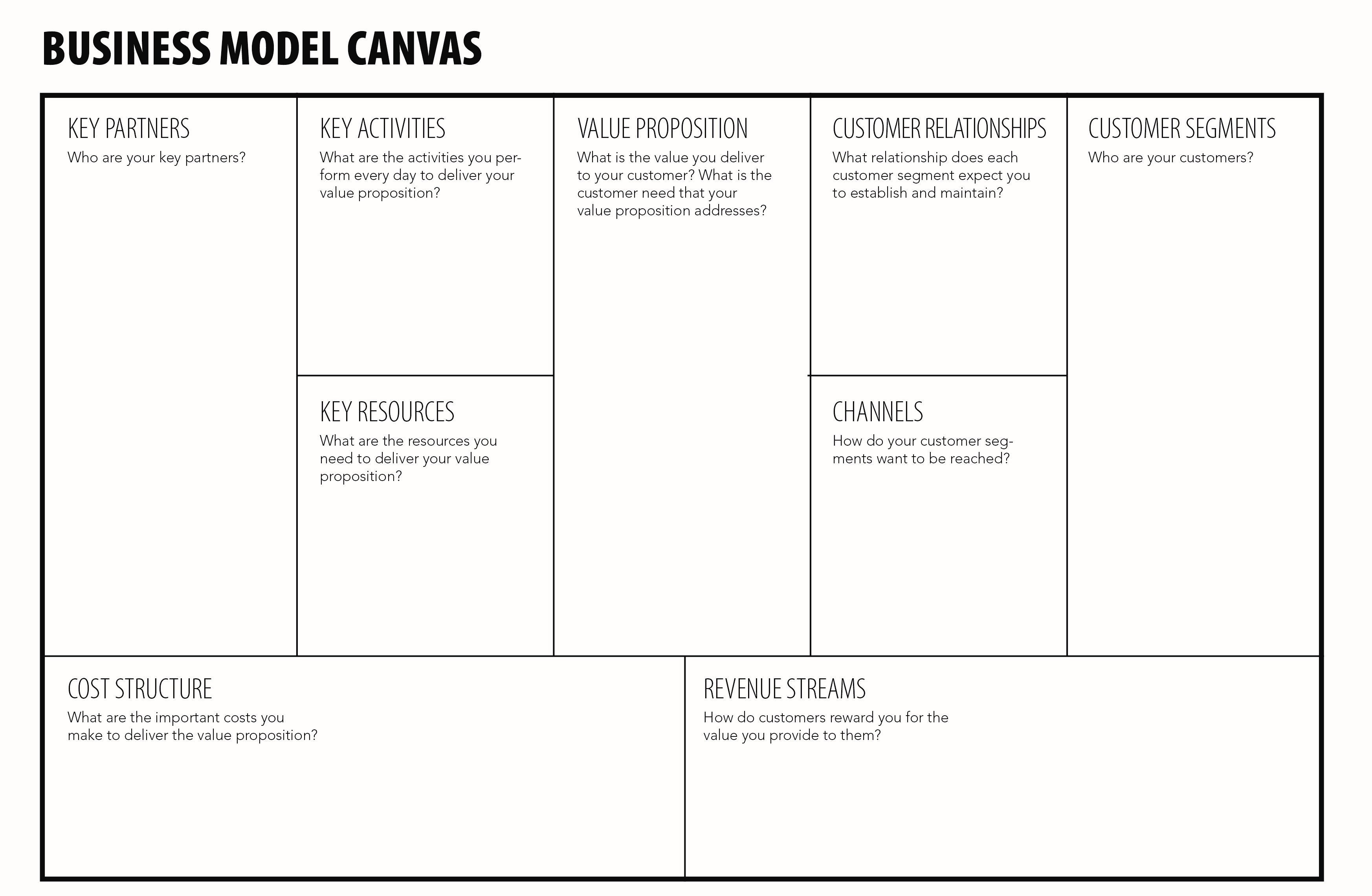
¶ What is it
The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a strategic management tool to quickly and easily define and communicate a business idea or concept.
It is a one page document which works through the fundamental elements of a business or product, structuring an idea in a coherent way.
¶ Template: Business Model Canvas Template (Word)
¶ Ansoff ‘s product/market grid
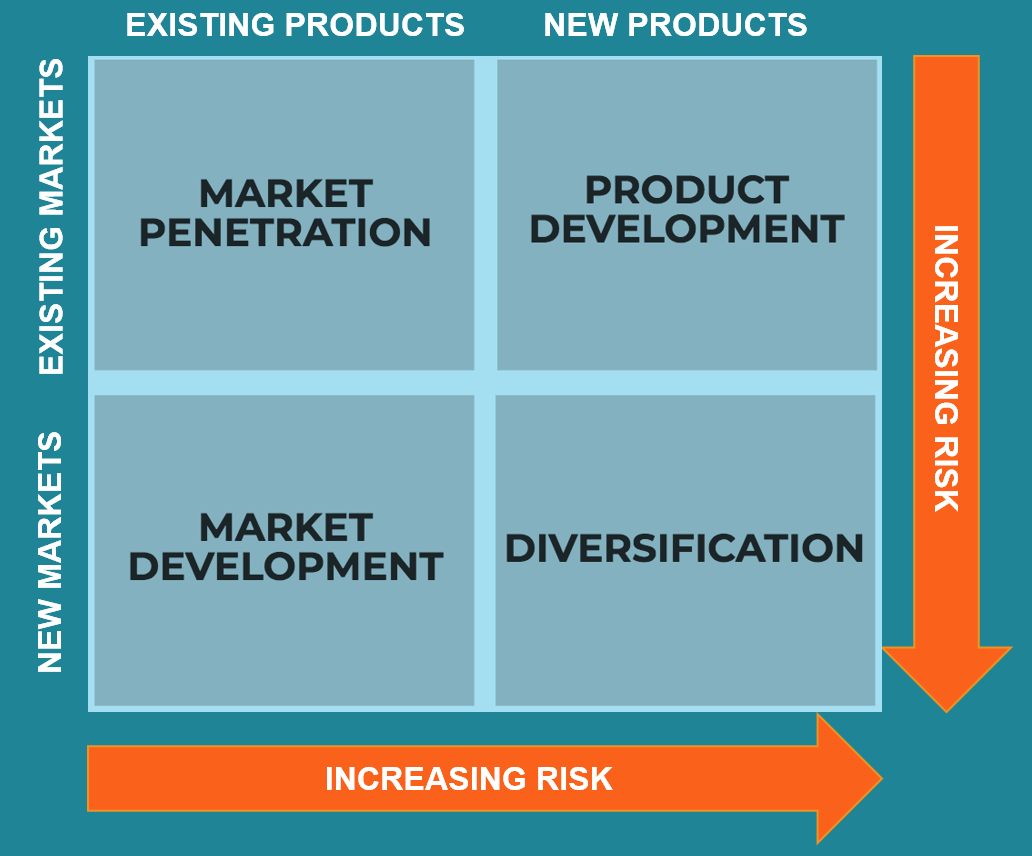
¶ What is it
The Ansoff Matrix, also called the Product/Market Expansion Grid, is a tool used by firms to analyze and plan their strategies for growth.
The matrix shows four strategies that can be used to help a firm grow and also analyzes the risk associated with each strategy.
¶ Porter’s 5 forces
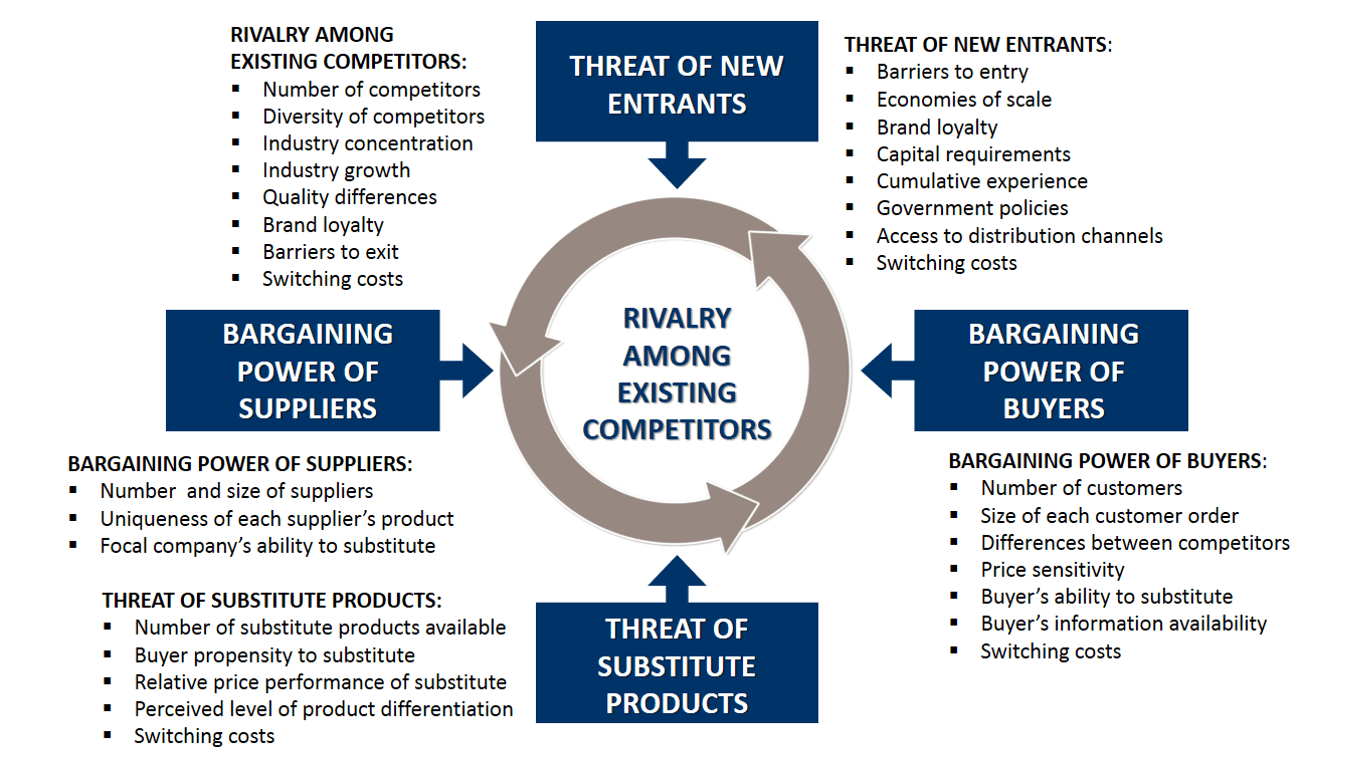
¶ What is it
Porter's Five Forces is a model that identifies and analyzes five competitive forces that shape every industry and helps determine an industry's weaknesses and strengths. Five Forces analysis is frequently used to identify an industry's structure to determine corporate strategy. Porter's model can be applied to any segment of the economy to understand the level of competition within the industry and enhance a company's long-term profitability.
¶ SWOT analysis
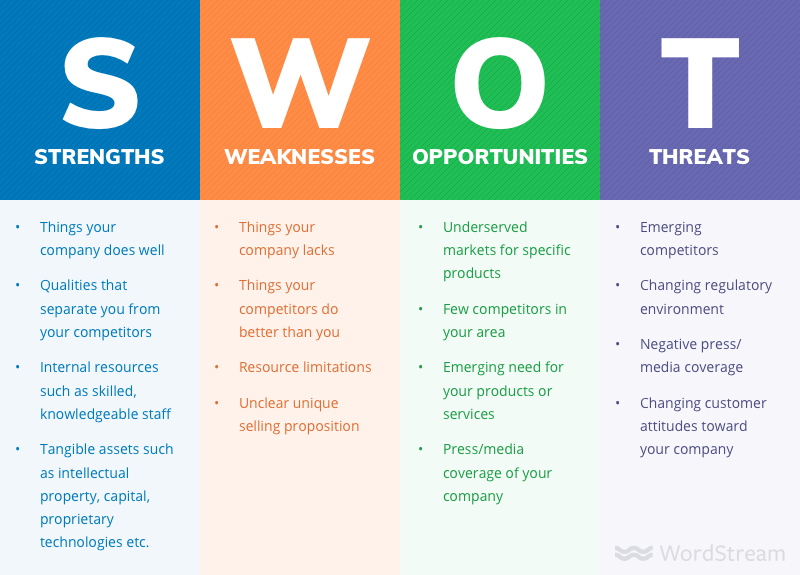
¶ What is it
SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis is a framework used to evaluate a company's competitive position and to develop strategic planning. SWOT analysis assesses internal and external factors, as well as current and future potential.
¶ Template: SWOT Template English (Excel)
¶ Confrontation matrix
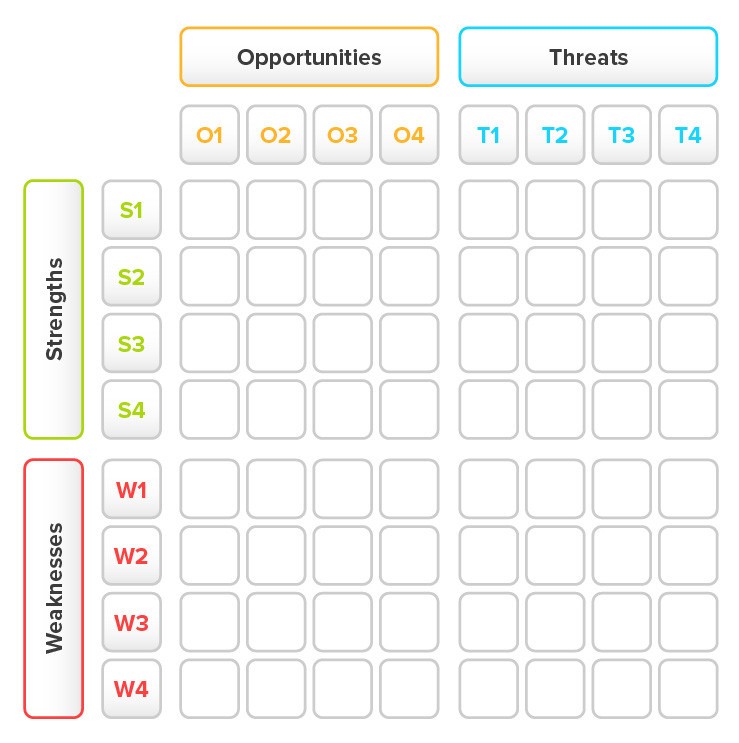
¶ What is it
A Confrontation Matrix is a tool which is used to further analyse the output of a SWOT analysis. It allows you to analyse each different combination of strength, weakness, opportunity, and threat. By doing this the aim is to identify the most important strategic issues the organization is facing.
¶ Template: Confrontatiematrix Template Dutch (Excel)
¶ Product Life Cycle (PLC)
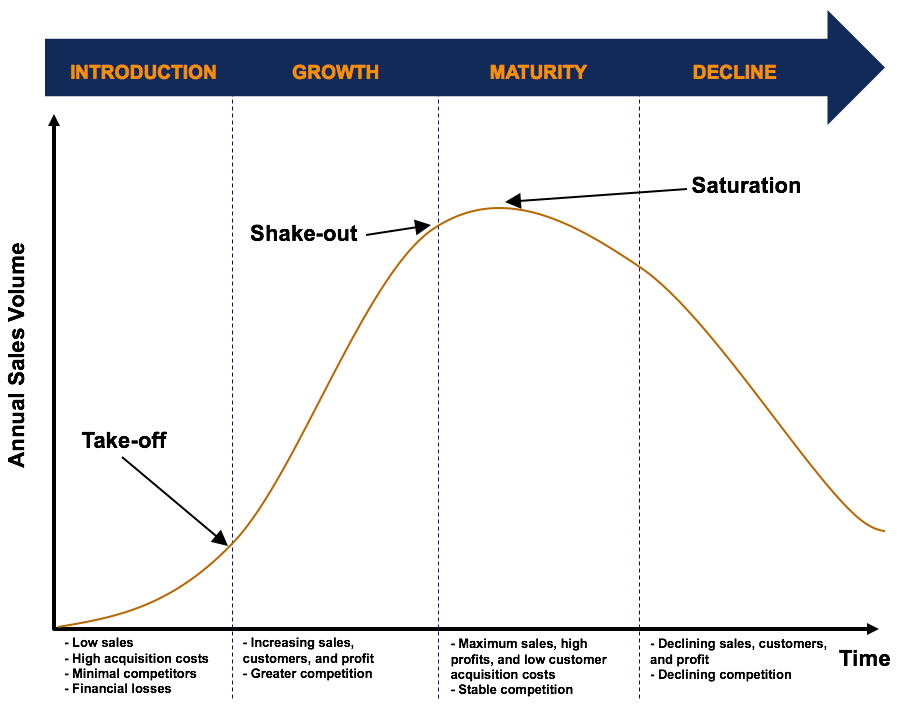
¶ What is it
The product life cycle (PLC) identifies and explains the stages that a product may go through from the moment it is launched on to the market to the moment it is withdrawn. Knowledge of the PLC can help identify important marketing environmental factors that managers should be aware of before they decide upon the most effective marketing effort.
¶ BCG matrix
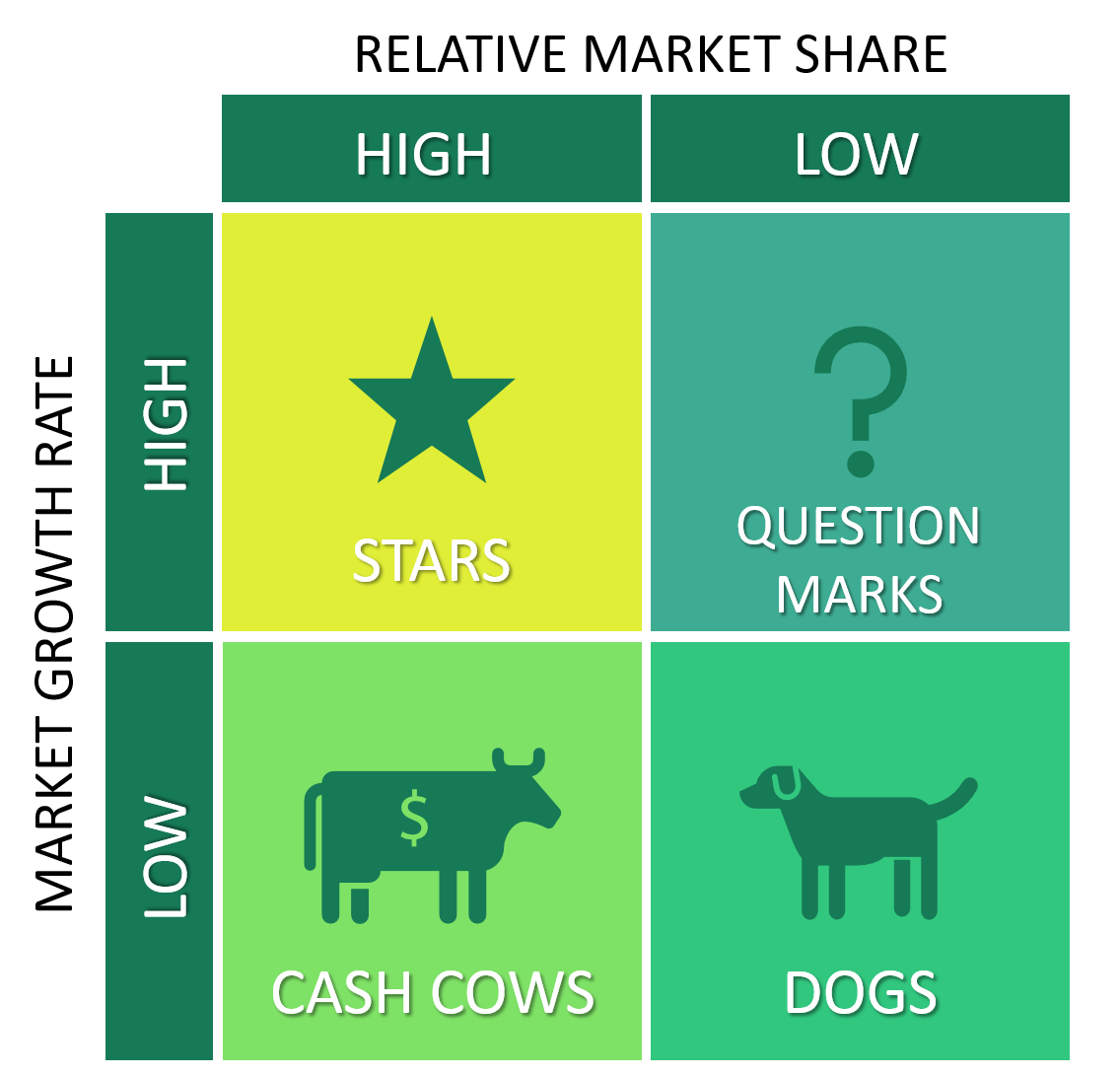
¶ What is it
The Boston Consulting group's product portfolio matrix (BCG matrix) is designed to help with long-term strategic planning, to help a business consider growth opportunities by reviewing its portfolio of products to decide where to invest, to discontinue or develop products. It's also known as the Growth/Share Matrix.
¶ Porter’s generic strategies
_strategies.png)
¶ What is it
Porter's generic strategies describe how a company pursues competitive advantage across its chosen market scope. There are three/four generic strategies, either lower cost, differentiated, or focus. A company chooses to pursue one of two types of competitive advantage, either via lower costs than its competition or by differentiating itself along dimensions valued by customers to command a higher price.
¶ Decision (SAF) matrix
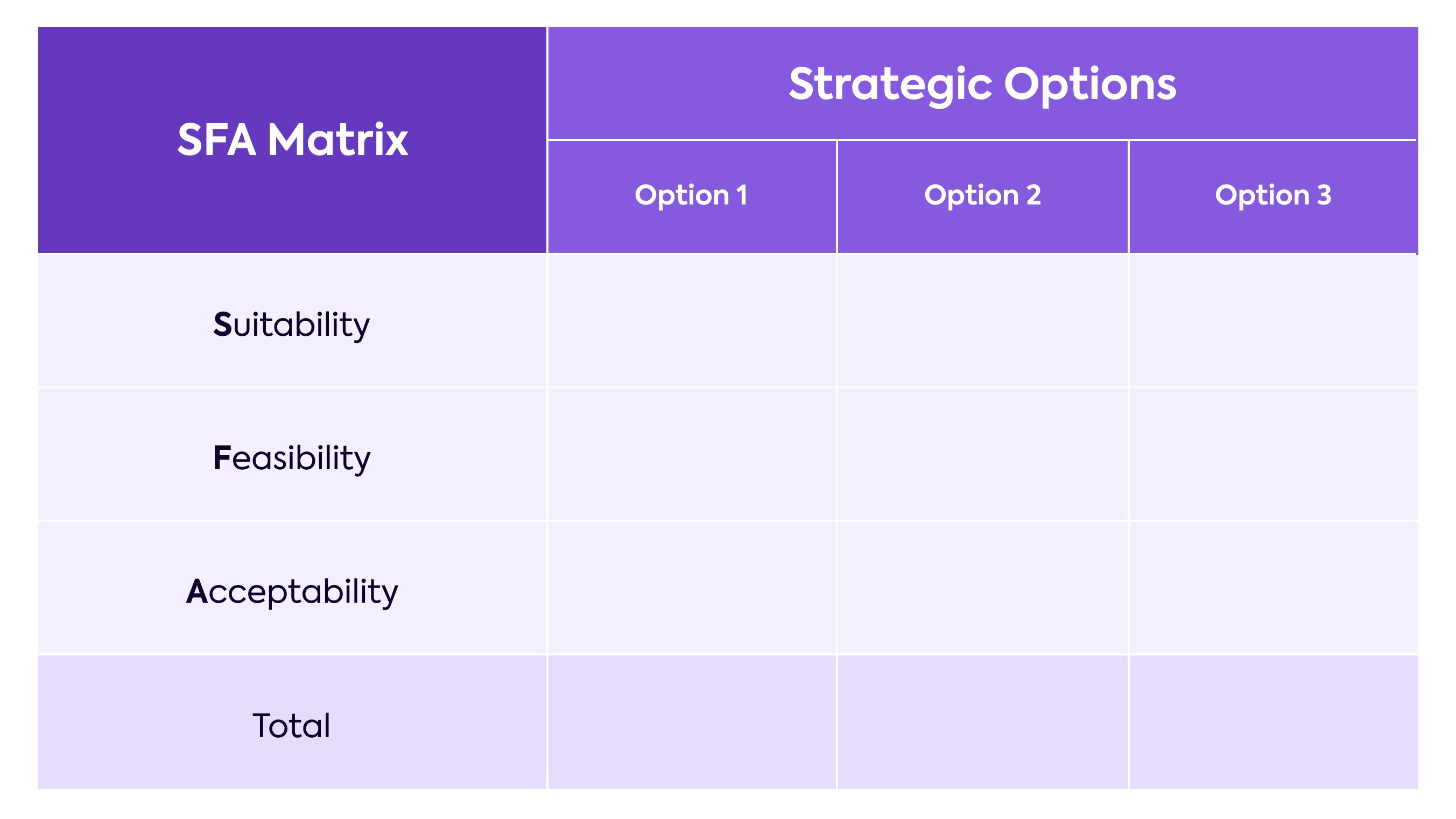
¶ What is it
The SFA Matrix is a framework to evaluate your strategic options in order to pick one. SFA stands for Suitability, Feasibility and Acceptability. These are the criteria areas in SAF Analysis used to judge and score each strategy.
¶ Template: TBA
¶ Stakeholder analysis
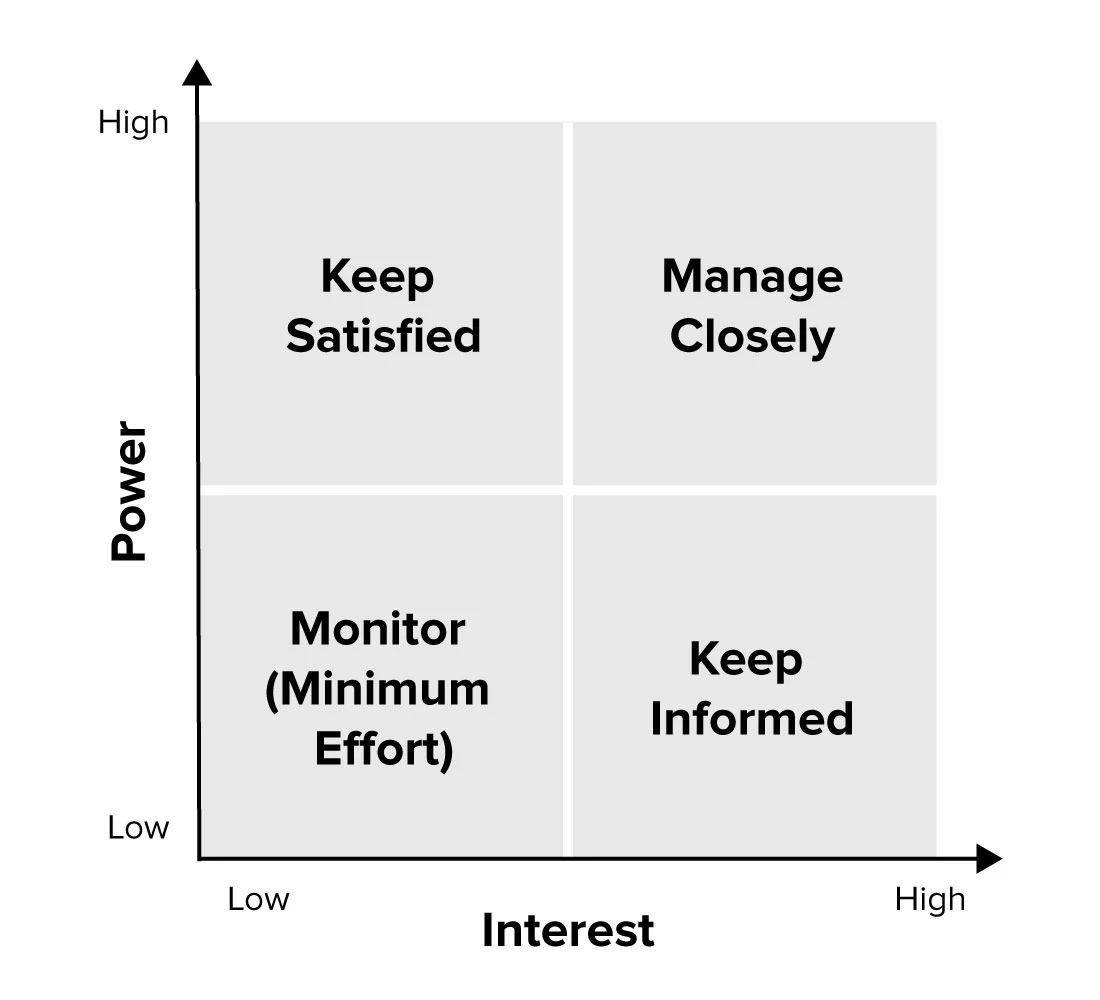
¶ What is it
A stakeholder analysis is a process of identifying people before the project begins. Grouping them according to their levels of participation, interest, and influence in the project. Then determining how best to involve and communicate each of these stakeholder groups throughout.
¶ Ishikawa/Fishbone diagram
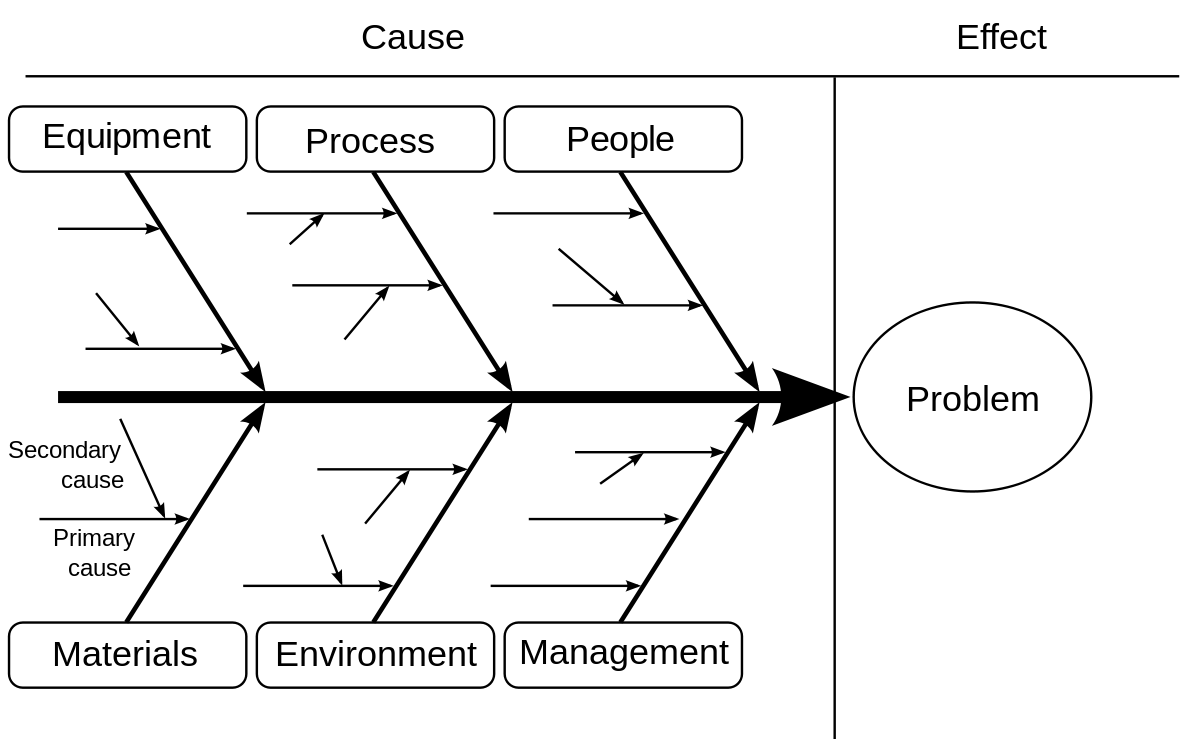
¶ What is it
An Ishikawa diagram is a diagram that shows the causes of an event and is often used in manufacturing and product development to outline the different steps in a process, demonstrate where quality control issues might arise and determine which resources are required at specific times.
¶ Operations Manager
¶ Input Transformation Output (ITO)

¶ What is it
The Input-Transform-Outcome (ITO) model seeks to describe the mechanisms by which outcomes are generated from outputs and, (as a by-product) how the two concepts are distinguished. This framework is later applied to all of the phases that define the life of a project, from initiation to outcome realisation.
¶ Business process re-design
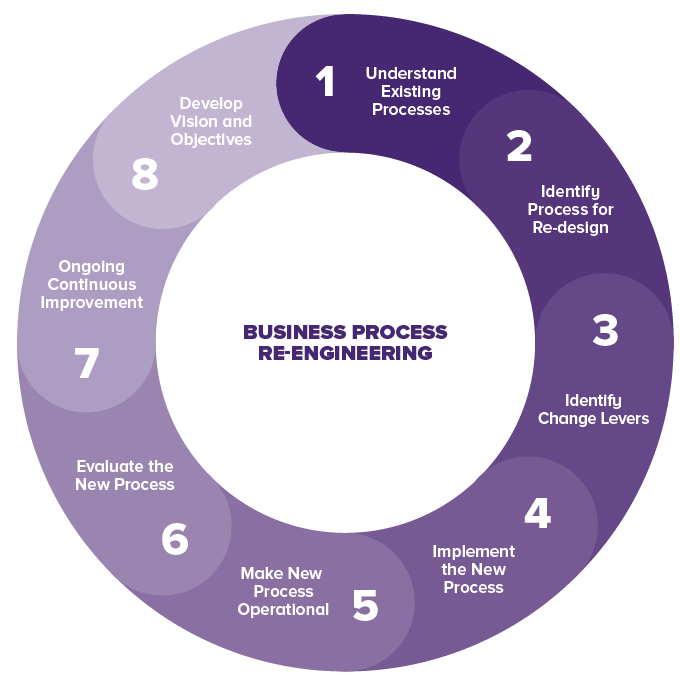
¶ What is it
The business process redesign refers to a complete overhaul of a company's key business process with the objective of achieving a quantum jump in performance measures such as return on investment (ROI), cost reduction, and quality of service.
¶ Cost of quality
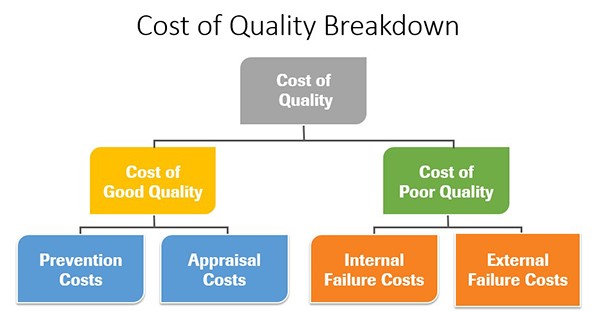
¶ What is it
Cost of Quality is a methodology used to define and measure where and what amount of an organization’s resources are being used for prevention activities and maintaining product quality as opposed to the costs resulting from internal and external failures.
¶ Lean 6 sigma
.jpg)
¶ What is it
Lean Six Sigma is a philosophy where the strategies of Lean and Six Sigma are combined. It drives customer satisfaction and bottom-line results by reducing variation, waste, and cycle time while promoting the use of work standardization and flow. It applies anywhere variation and waste exist, and every employee should be involved
¶ Risk management
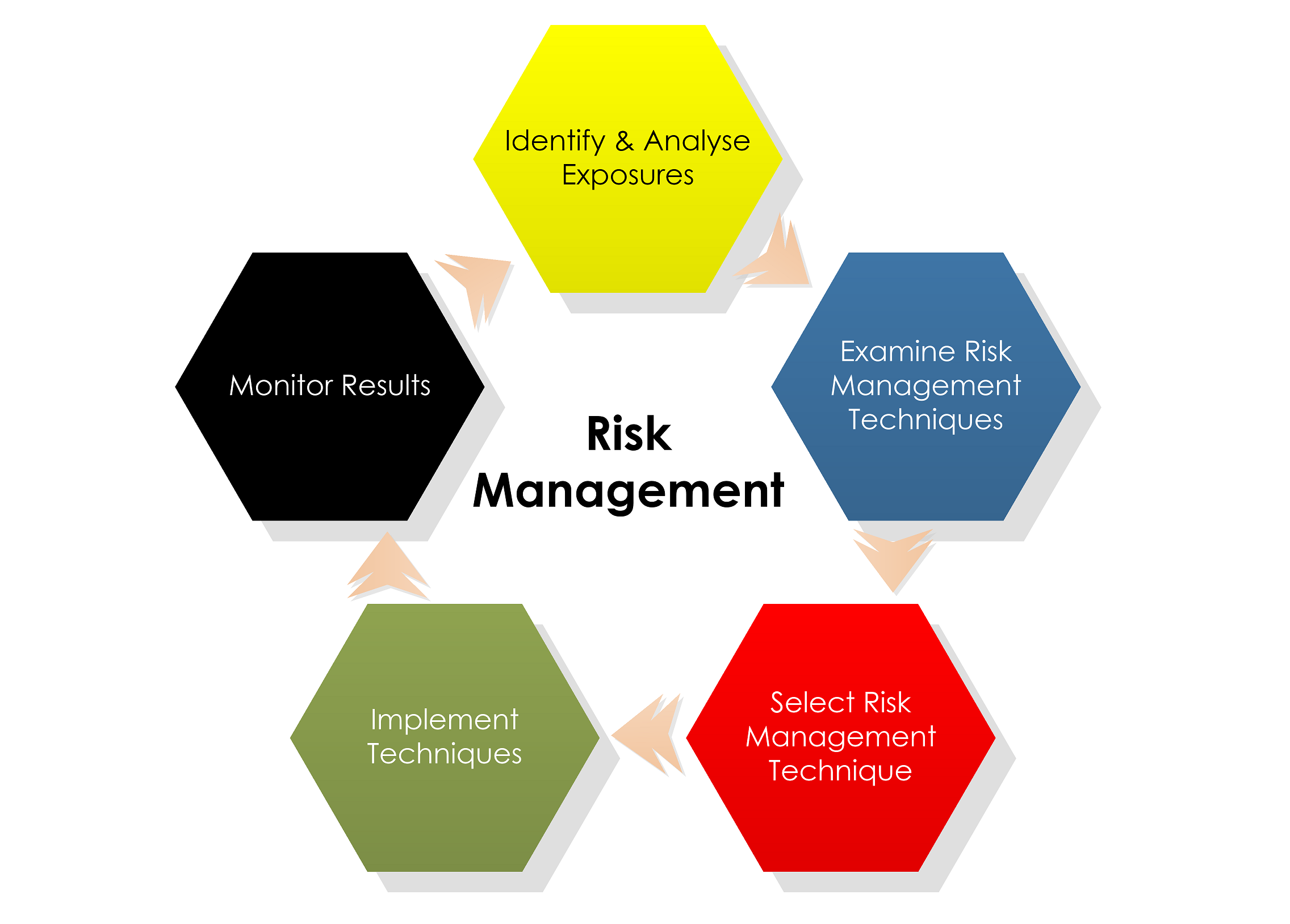
¶ What is it
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing and controlling threats to an organization's capital and earnings. These threats, or risks, could stem from a wide variety of sources, including financial uncertainty, legal liabilities, strategic management errors, accidents and natural disasters.
¶ Marketing Manager
¶ Segmentation Targeting Positioning (STP)
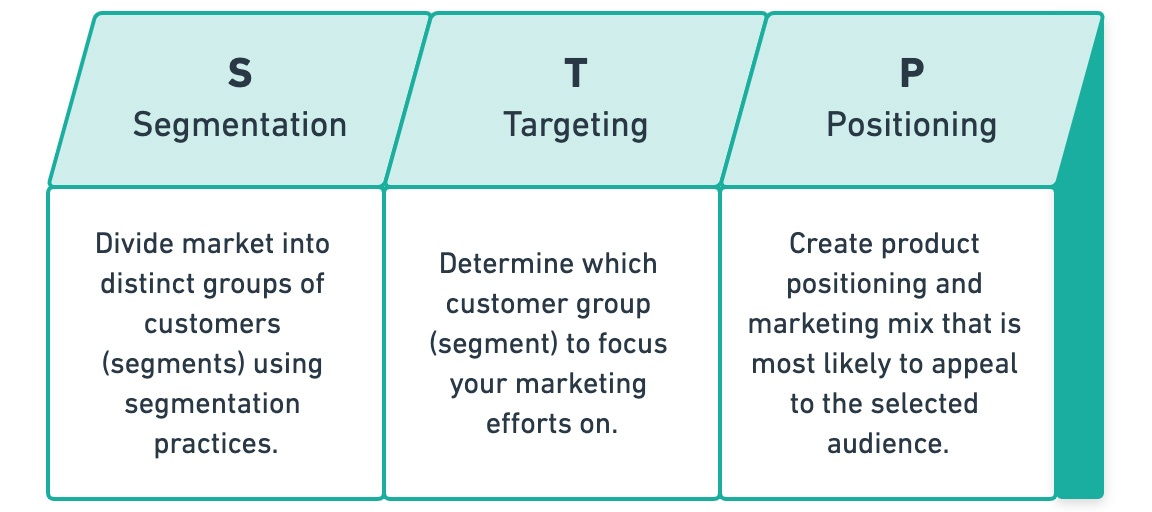
¶ What is it
STP is a three-step model that examines your products or services as well as the way you communicate their benefits to specific customer segments. You segment your market, target select customer segments with marketing campaigns tailored to their preferences, and adjust your positioning according to their desires and expectations.
¶ Roger’s diffusion/adoption cycle
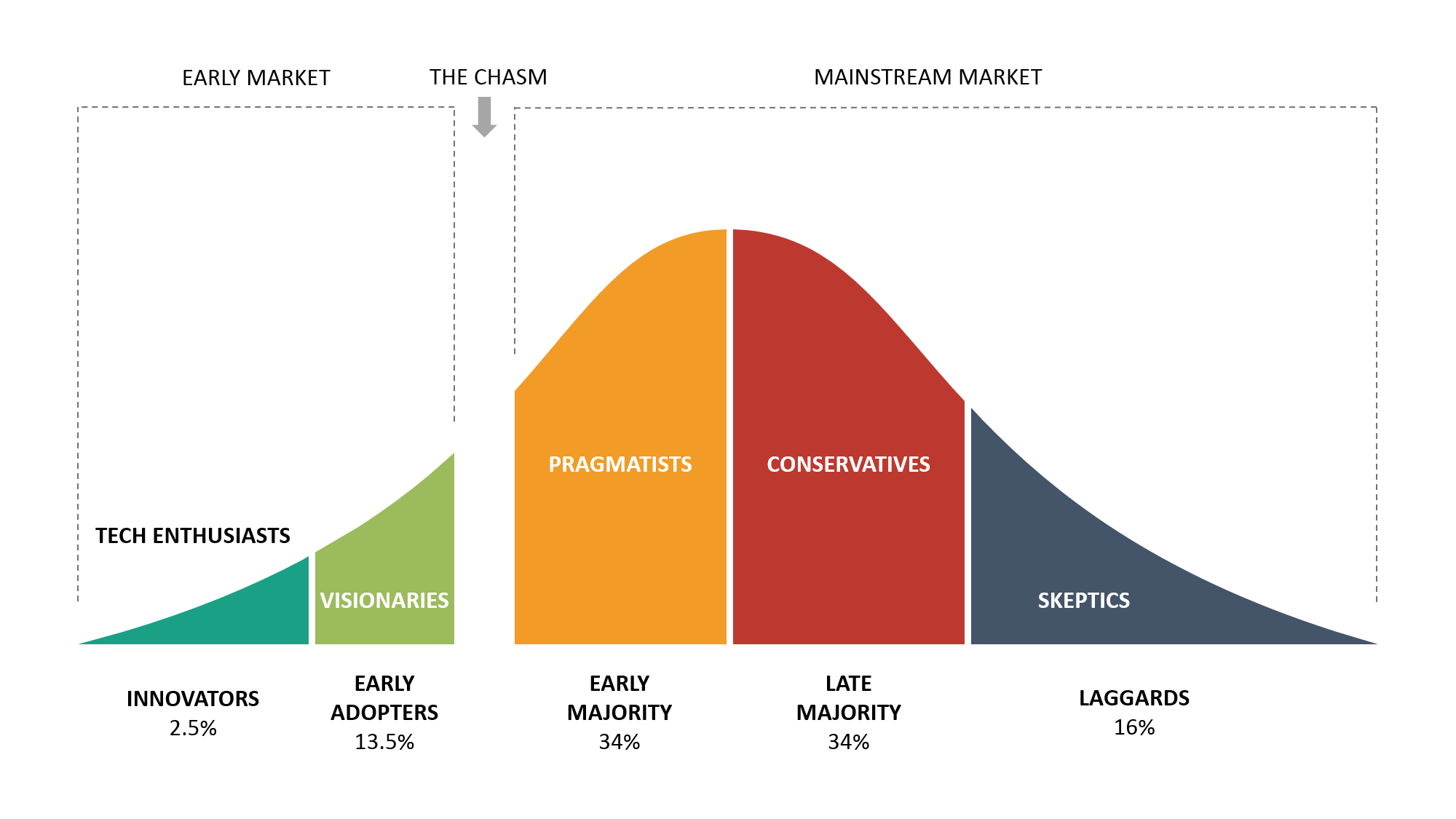
¶ What is it
The diffusion of innovation is the process by which new products are adopted (or not) by their intended audiences. It allows designers and marketers to examine why it is that some inferior products are successful when some superior products are not.
¶ Market entry modes
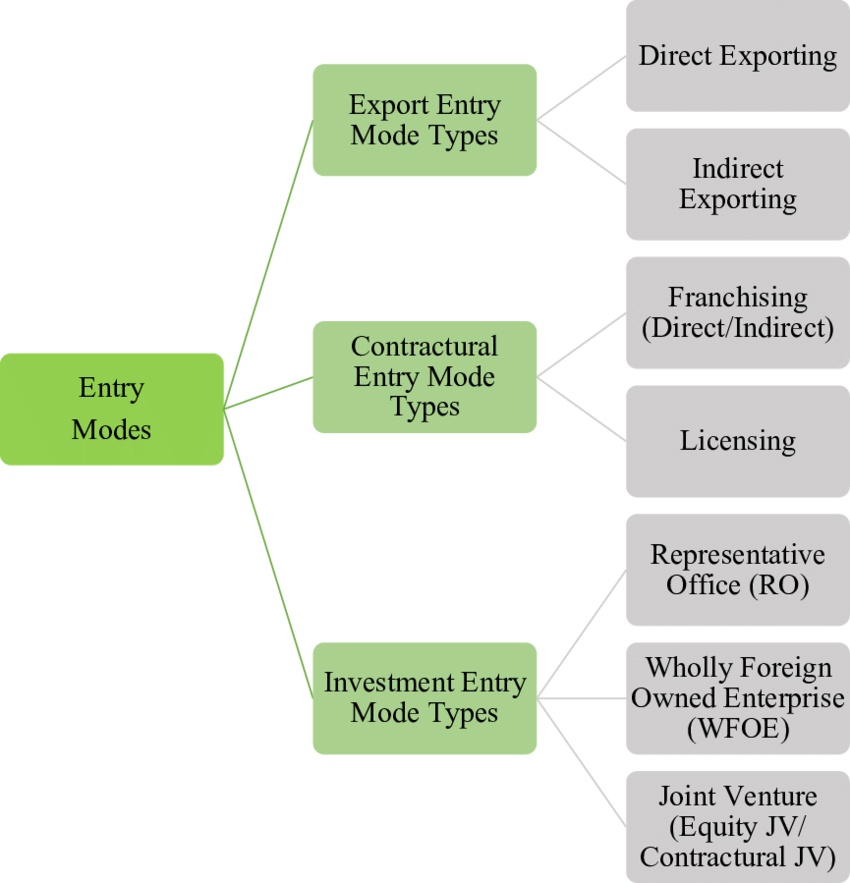
¶ What is it
Foreign market entry modes are the ways in which a company can expand its services into a non-domestic market.
¶ Marketing plan
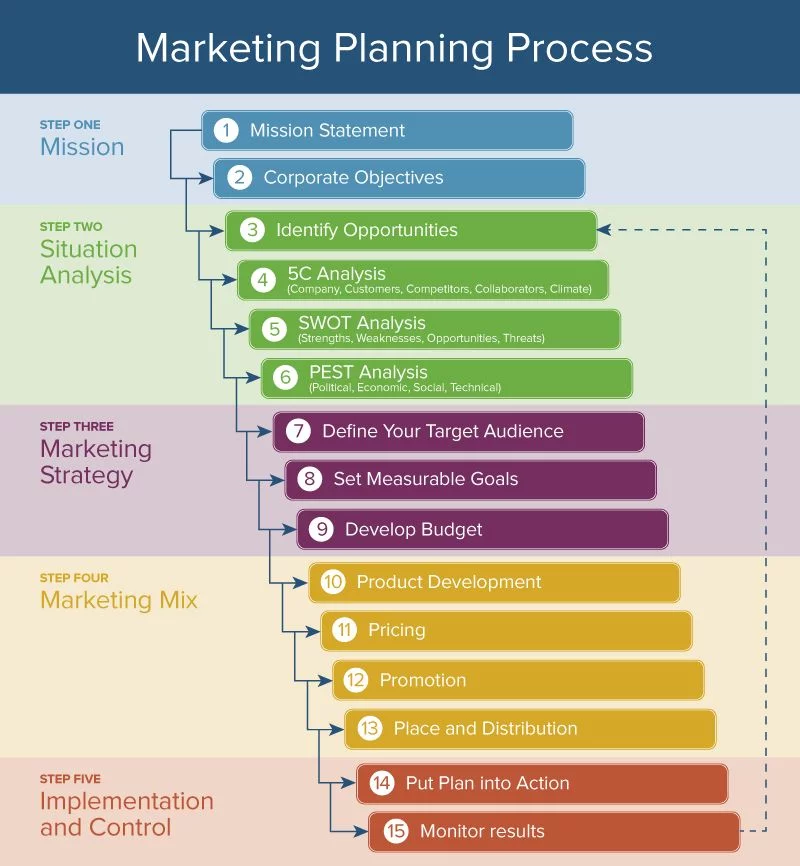
¶ What is it
The marketing planning process is a systematic approach for developing marketing goals, strategy and implementation tactics. It may be adapted to a wide variety of situations, from the launch of a new firm or practice area to the repositioning of an existing firm. Even the routine planning of new business development activities.
¶ Marketing communication plan
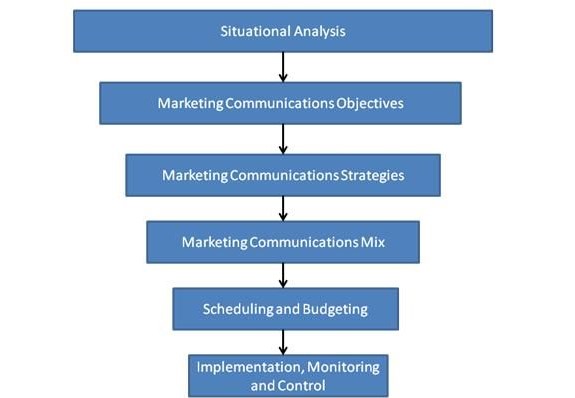
¶ What is it
A marketing communications plan, or a marcom plan, is a strategy for informing your target customer audience about your product or service. When the plan is sold, it must incorporate the target market, or the specific population identified for a product or service.!
¶ Finance Manager
¶ Value based management
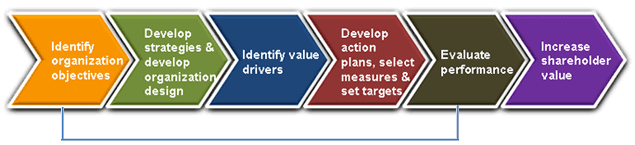
¶ What is it
Value Based Management (VBM) is the management philosophy and approach that enables and supports maximum value creation in organizations, typically the maximization of shareholder value. VBM encompasses the processes for creating, managing, and measuring value.
¶ Payback period and ROI
¶ What is it
¶ Payback period
The payback period refers to the amount of time it takes to recover the cost of an investment. Simply put, the payback period is the length of time an investment reaches a break-even point. The desirability of an investment is directly related to its payback period. Shorter paybacks mean more attractive investments.
¶ ROI
Return on Investment (ROI) is a performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or compare the efficiency of a number of different investments. ROI tries to directly measure the amount of return on a particular investment, relative to the investment's cost.
¶ Capital Budgetting
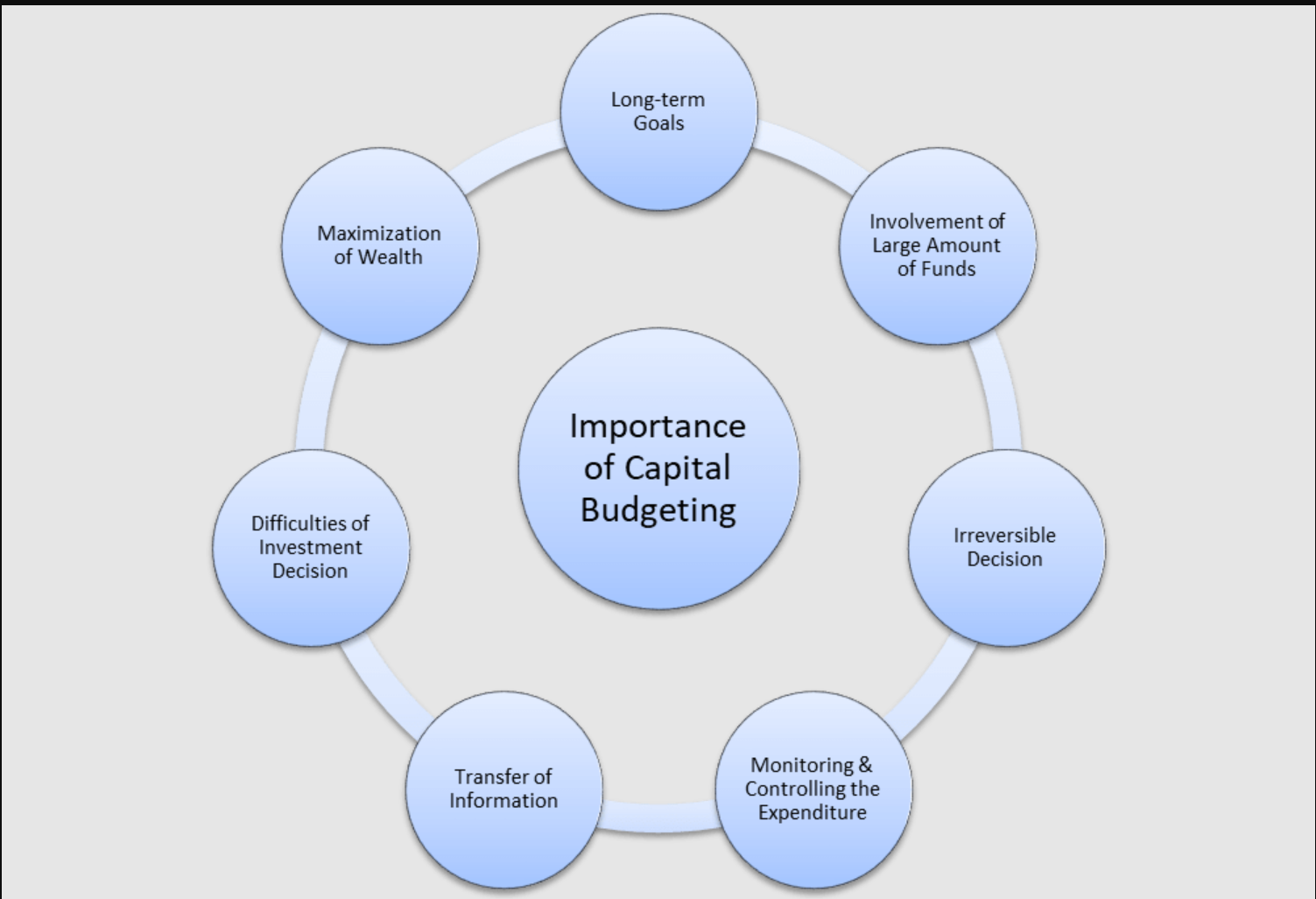
¶ What is it
Capital budgeting is the process a business undertakes to evaluate potential major projects or investments. Construction of a new plant or a big investment in an outside venture are examples of projects that would require capital budgeting before they are approved or rejected, it creates accountability and measurability.
¶ Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) and Net Present Value (NPV)
¶ What is it
¶ Discounted cash flow (DCF)
The DCF assists in analysing an investment and determining its value, and how valuable it would be in the future. The DCF method makes it clear how long it would take you to get returns.
¶ Net Present Value (NPV)
The Net Present Value compares the value of the investment amount today to its value in the future, it is useful in comparing internal and external investments.
¶ Financial statement analysis
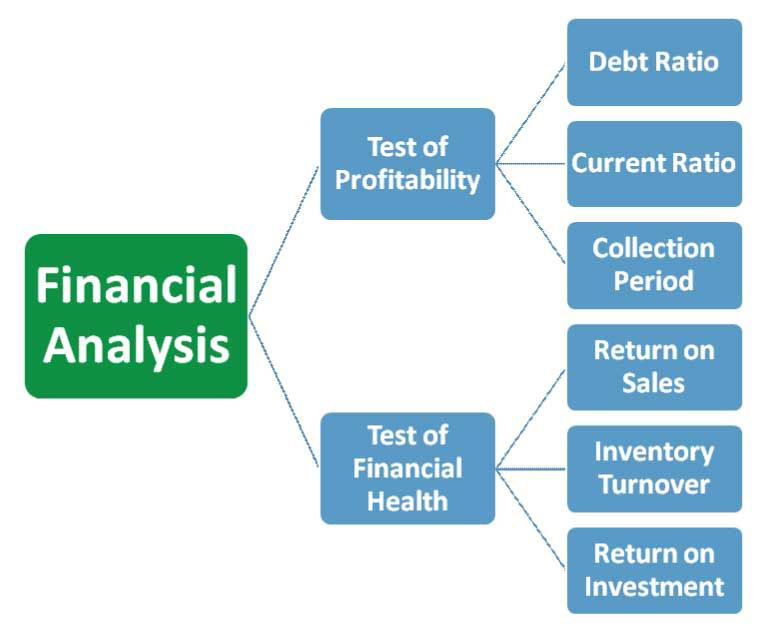
¶ What is it
Financial statement analysis is the process of analyzing a company's financial statements for decision-making purposes. External stakeholders use it to understand the overall health of an organization as well as to evaluate financial performance and business value.
¶ Human Resource Manager
¶ Belbin’s team roles
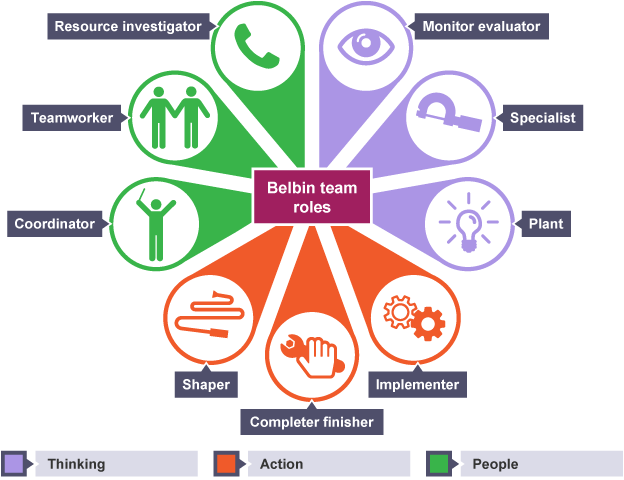
¶ What is it
The underlying idea of identifying Belbin Team Roles is to engage and develop the talent that is already around you. You can use Team Roles to help build high-performing teams, maximise working relationships, and to enable people to learn about themselves.
¶ ADKAR
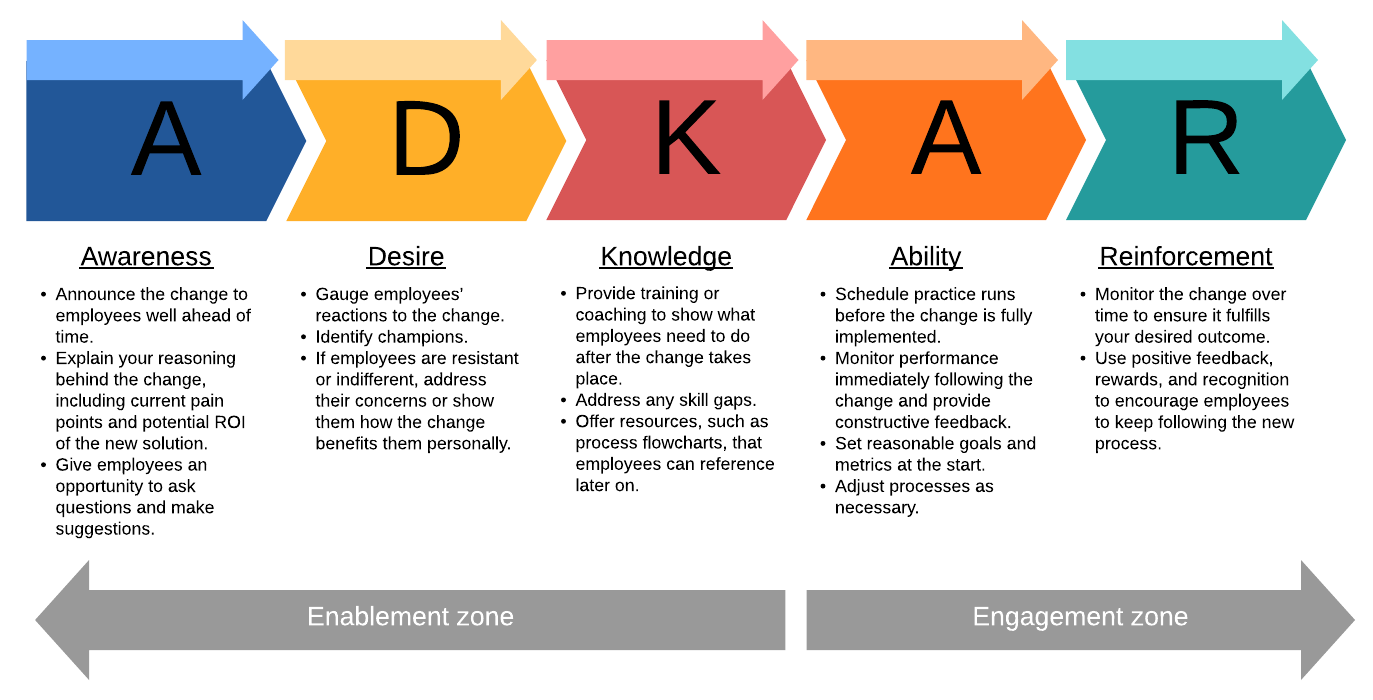
¶ What is it
The ADKAR model is a 5-step framework that helps deal with the people-aspect of change management. ADKAR is an acronym that represents the five tangible and concrete outcomes that people need to achieve for lasting change: awareness, desire, knowledge, ability and reinforcement.
¶ Lewis culture model
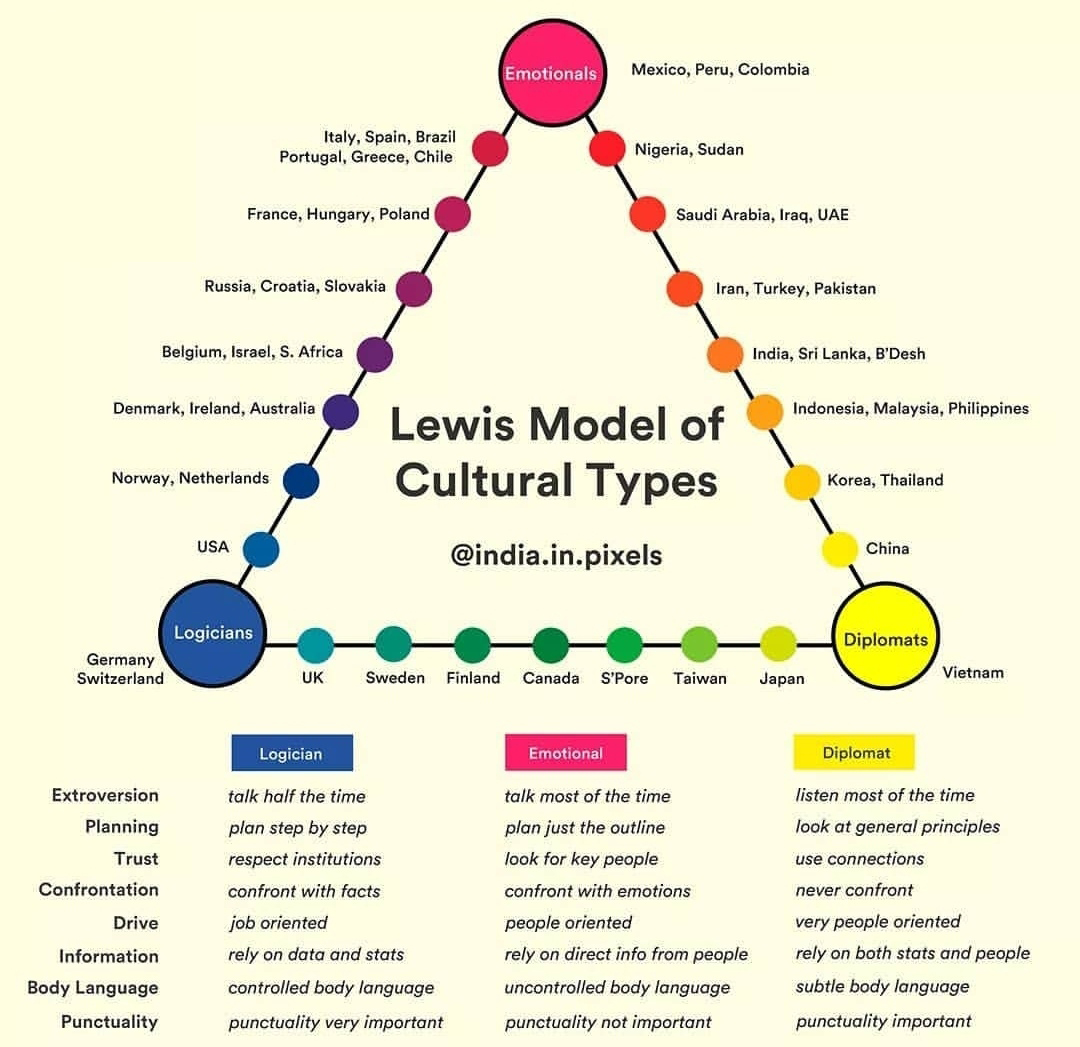
¶ What is it
The Lewis Model is designed to indicate with which particular cultural group an individual would have empathy with. Lewis named his three typologies Linear-active, Multi-active and Reactive. The diagram indicates the relative positioning of each national culture in general terms of its linear-active, multi-active or reactive nature.
¶ Balanced Scorecard (BSC)
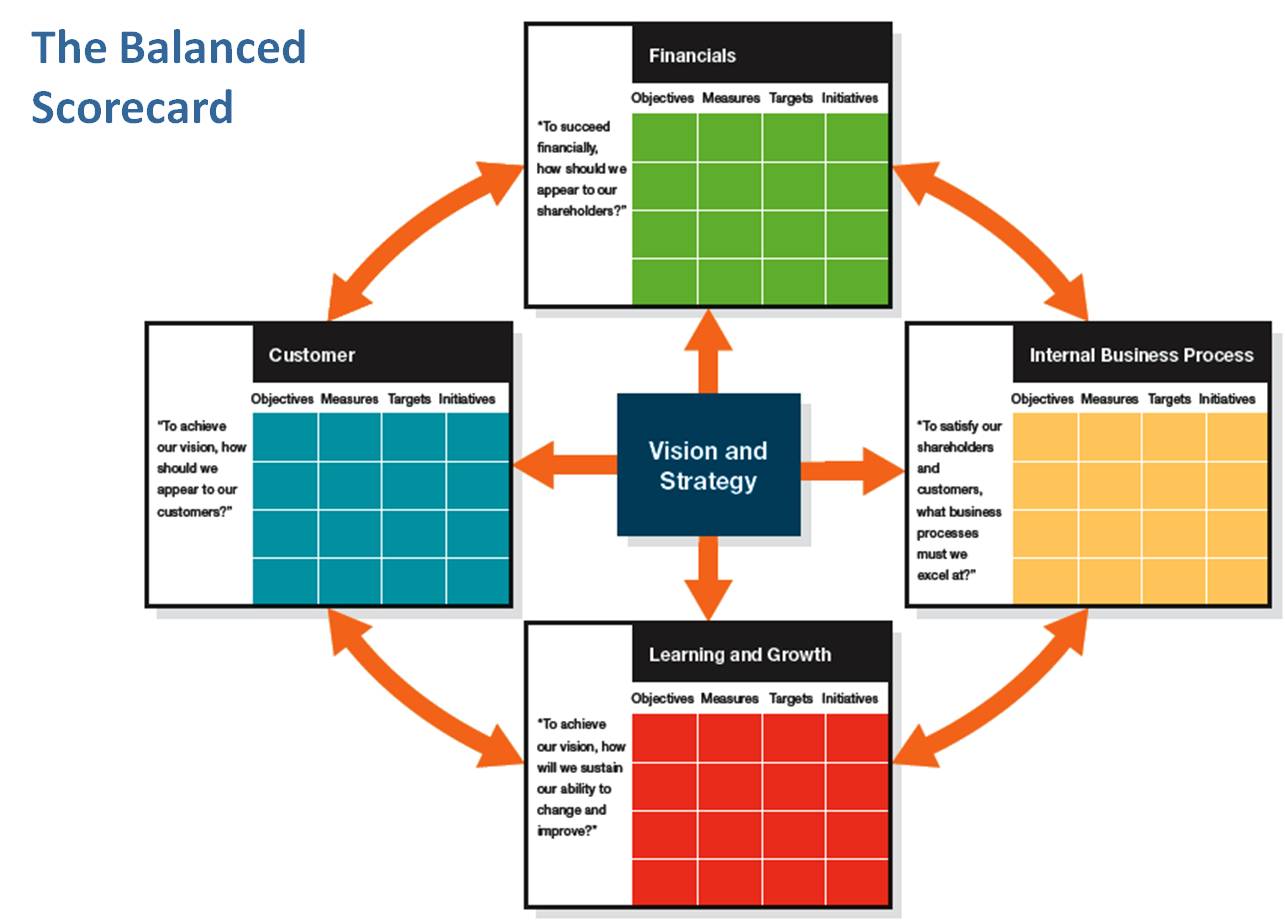
¶ What is it
A balanced scorecard is a strategic management performance metric used to identify and improve various internal business functions and their resulting external outcomes. Balanced scorecards are used to measure and provide feedback to organizations.
¶ Hersey & Blanchard leadership model
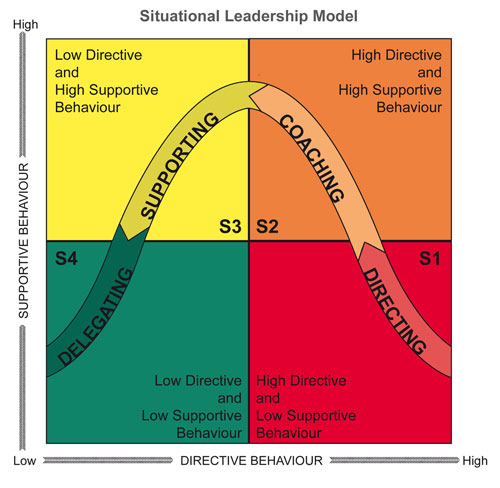
¶ What is it
The Hersey-Blanchard Model is a leadership model that focuses on the ability and willingness of individual employees.
By evaluating each employee's ability and experience, leaders can adapt their leadership methods to encourage professional development in their employees.
¶ Kotter’s 8 step change model
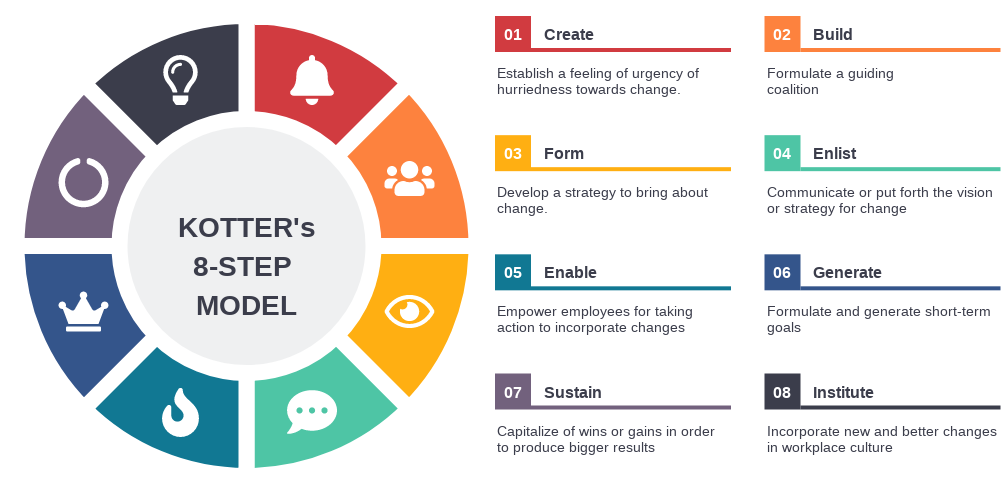
¶ What is it
Kotter’s 8 step change model is a framework for successfully implementing organizational change. The purpose of Kotter's 8-step model is to create a sensible vision. A clear and achievable vision can help people understand why you're asking them to change. The initiative is likely to be complicated and often difficult to understand.
¶ Goleman’s leadership style

¶ What is it
The Goleman Leadership Styles (or the six emotional leadership styles) are styles that leaders can take to make sure of a healthy working environment. According to the model, leaders should have the ability to deal with the changing environment on the work floor. The model is for this reason associated with emotional intelligence.
¶ Others
¶ Gantt chart
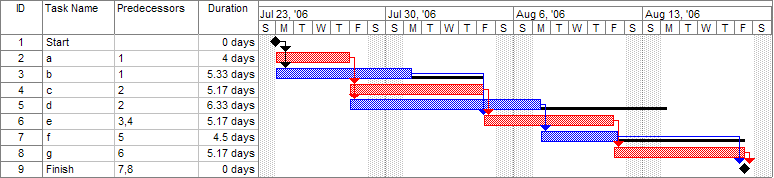
¶ What is it
A Gantt chart is a graphical depiction of a project schedule. It's is a type of bar chart that shows the start and finish dates of several elements of a project that include resources, milestones, tasks, and dependencies.
¶ DESTEP analysis

¶ What is it
A DESTEP Analysis is a framework used to understand the external environment and the issues that may impact you. DESTEP stands for Demographic, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Ecological and Political/Legal. These are the six categories you use to list factors that could impact your business.
¶ PESTEL analysis
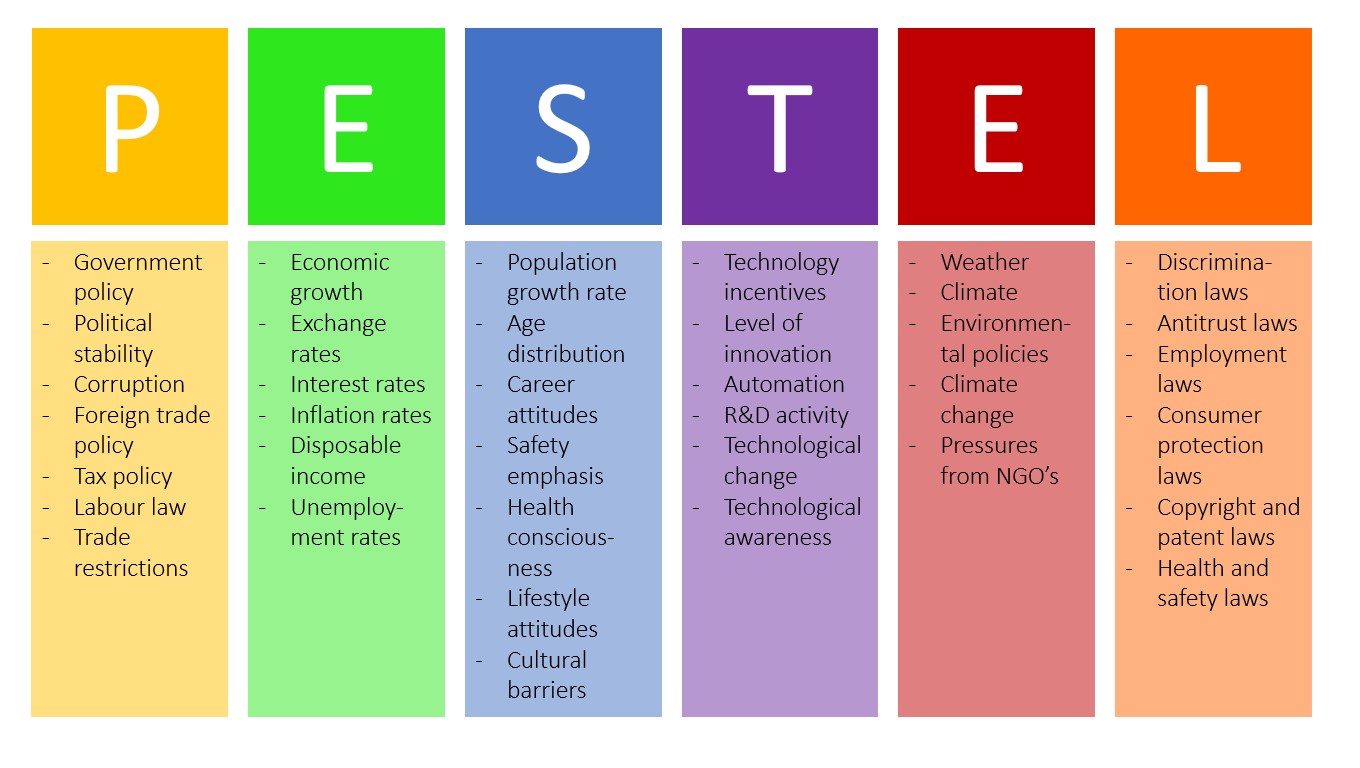
¶ What is it
A PESTEL analysis is a framework to analyse the key factors (Political, Economic, Sociological, Technological, Legal and Environmental) influencing an organisation from the outside. It offers people professionals insight into the external factors impacting their organisation.
¶ VRIO analysis
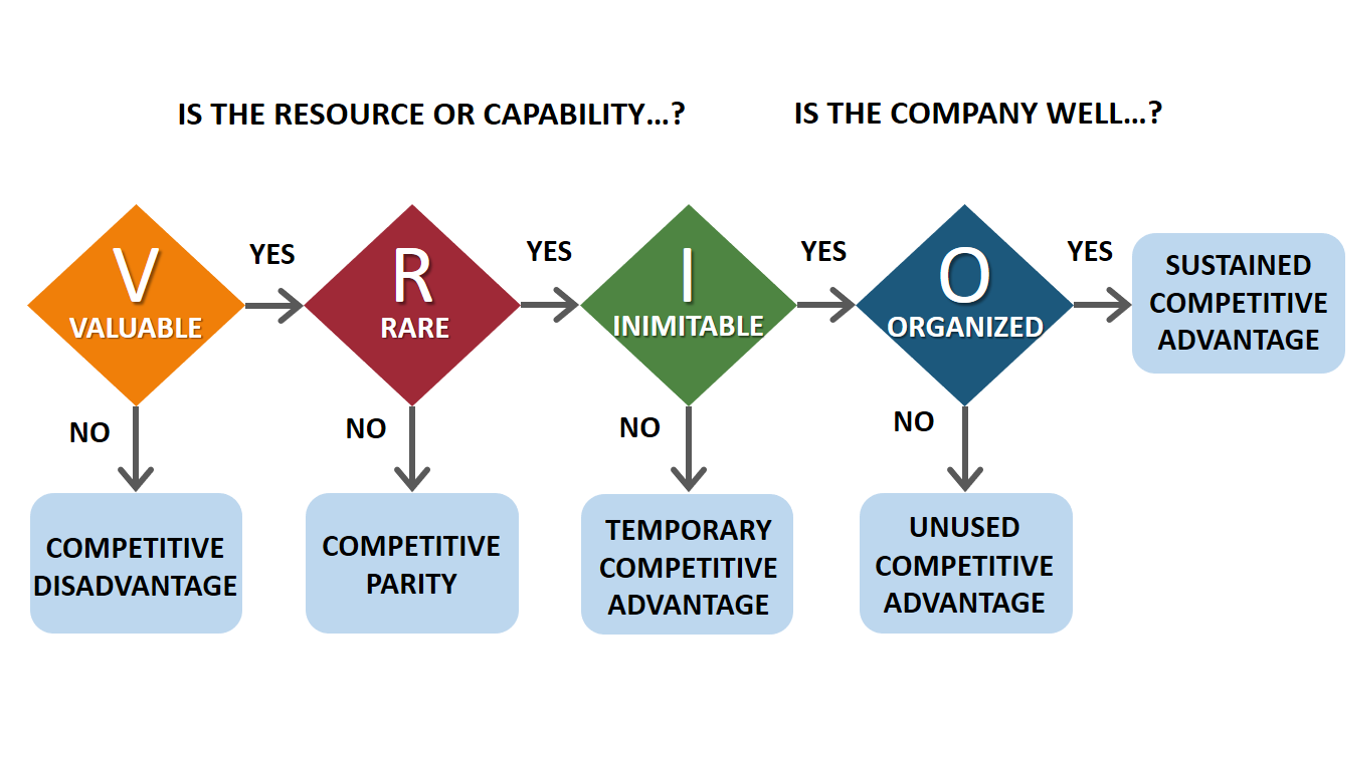
¶ What is it
VRIO analysis is a complement to a PESTEL analysis (which assesses macro-environment). VRIO is used to assess the situation inside the organization (enterprise) - its resources, their competitive implication and possible potential for improvement in the given area or for a given resource.
¶ 7s model McKinsey
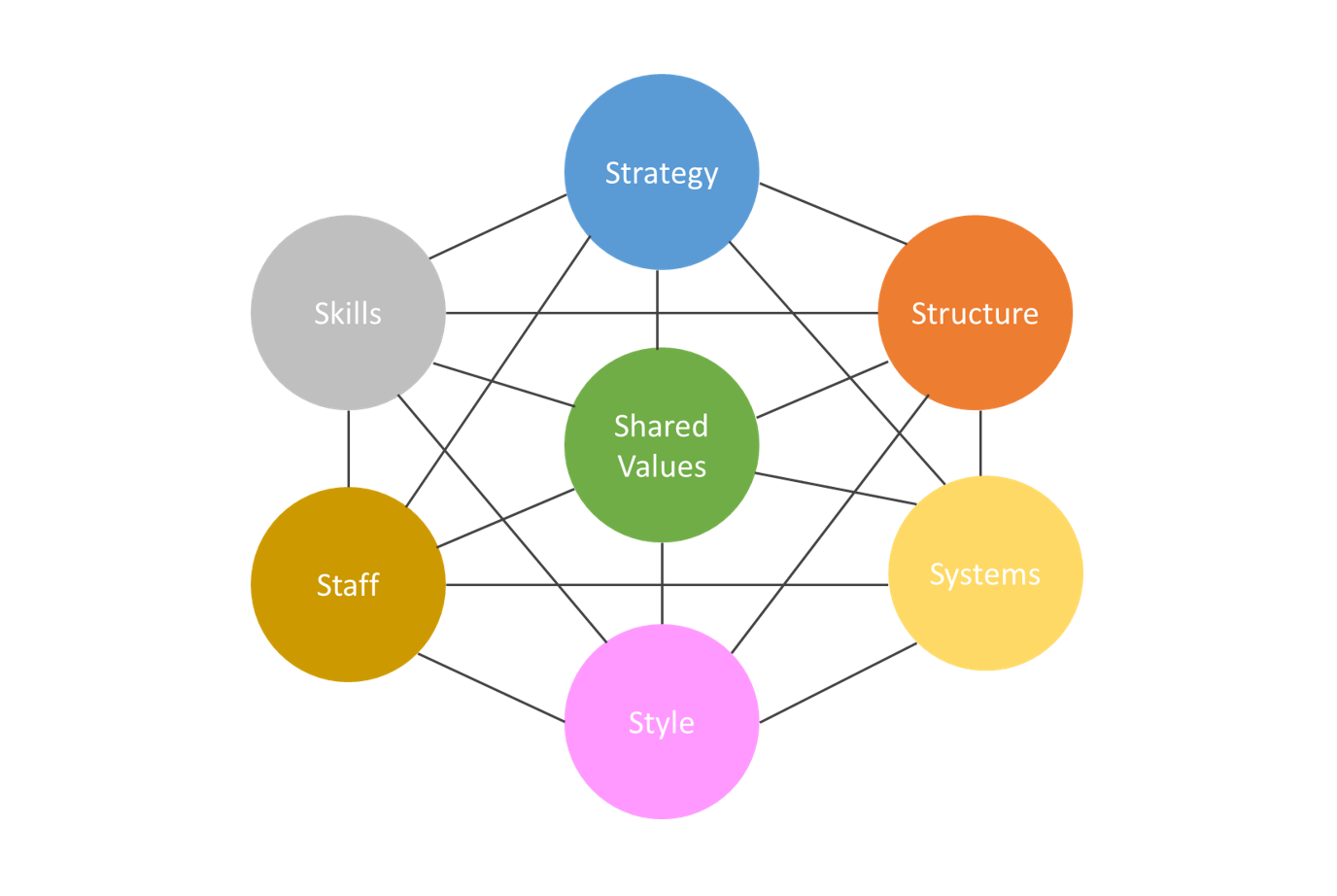
¶ What is it
McKinsey 7s model. is a tool that analyzes firm's organizational design by looking at 7 key internal elements: strategy, structure, systems, shared values, style, staff and skills, in order to identify if they are effectively aligned and allow organization to achieve its objectives.
¶ Gap analysis
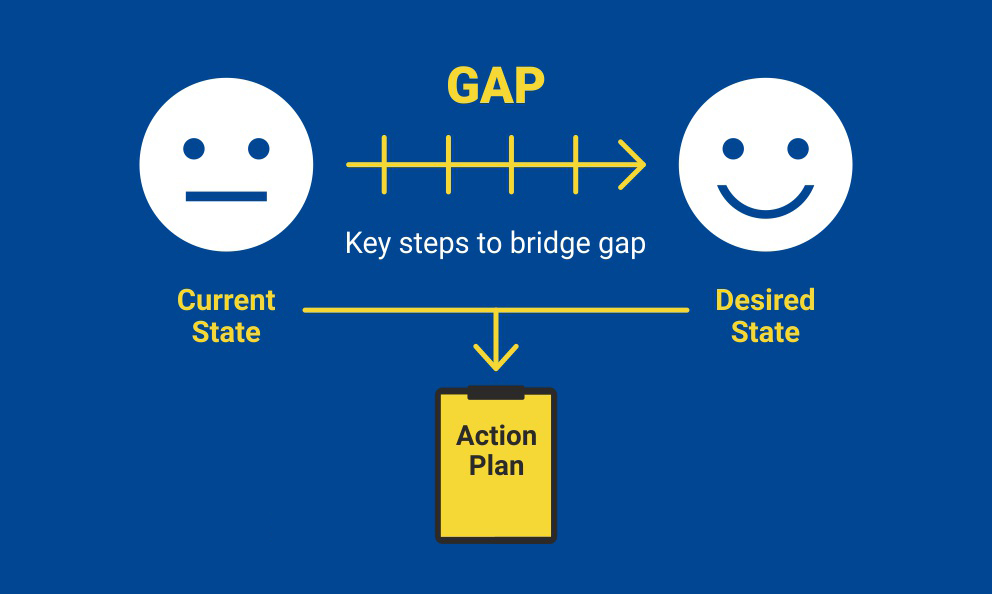
¶ What is it
A gap analysis is a method of assessing the differences in performance between a business' information systems or software applications to determine whether business requirements are being met and, if not, what steps should be taken to ensure they are met successfully.
¶ Tracey and Wiersema
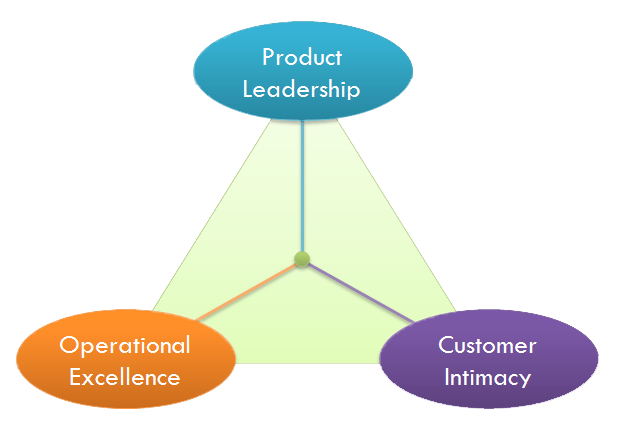
¶ What is it
To succeed in the marketplace, companies must embrace a competitive strategy. Michael Treacy and Fred Wiersma describe three generic competitive strategies, or value disciplines: operational excellence, customer intimacy and product leadership. The author’s main premise is that companies must choose—and then achieve—market leadership in one of the three disciplines, and perform to an acceptable level in the other two.
¶ Pareto analysis

¶ What is it
Pareto Analysis is a statistical technique in decision-making used for the selection of a limited number of tasks that produce significant overall effect. It uses the Pareto Principle (also known as the 80/20 rule) the idea that by doing 20% of the work you can generate 80% of the benefit of doing the entire job.
¶ Plan Do Check Act (PDCA)
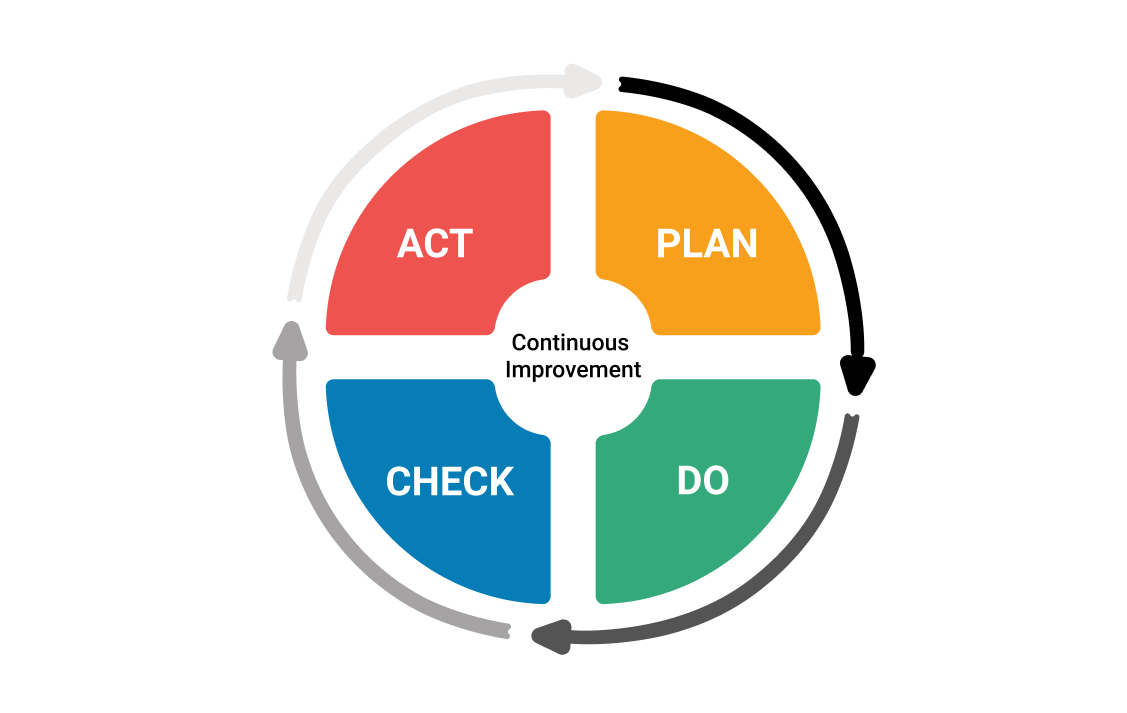
¶ What is it
The Deming Cycle, or PDCA Cycle (also known as PDSA Cycle), is a continuous quality improvement model consisting out of a logical sequence of four repetitive steps for continuous improvement and learning: Plan, Do, Check (Study) and Act.